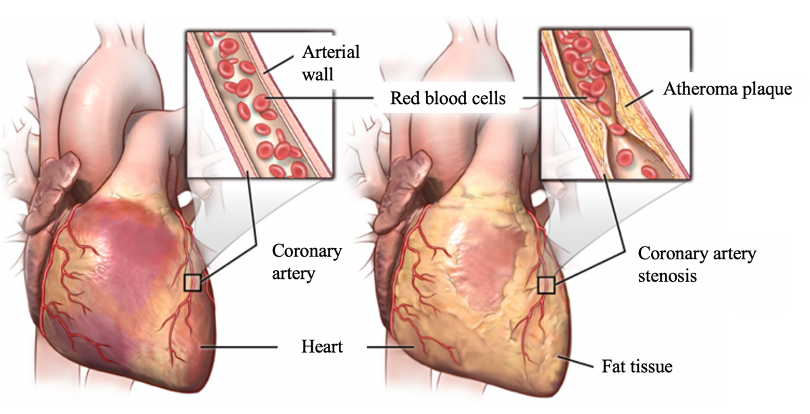
What is coronary atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis is a chronic disease that results from cholesterol / fat deposits in the coronary arteries.
These changes lead to internal diameter narrowing of the coronary artery, called stenosis, limiting the blood supply to the heart muscle and thus leading to the appearance of angina pectoris. A prolonged occlusion of the artery leads to the occurrence of a myocardial infarction / heart attack.
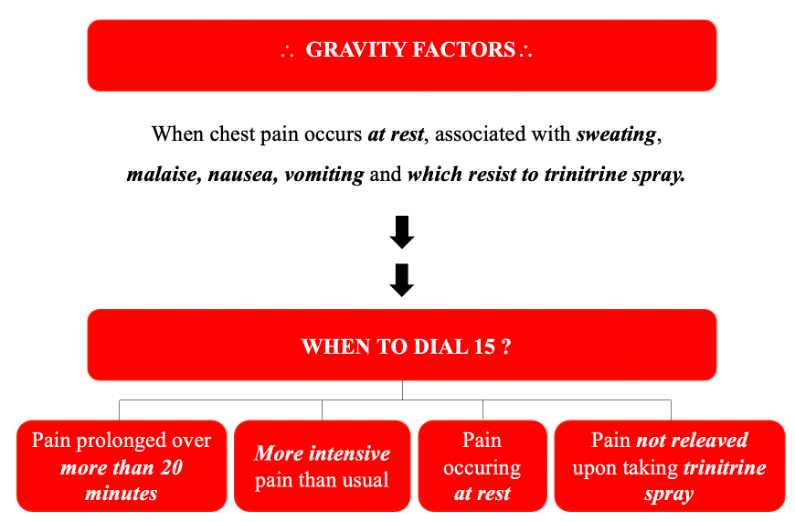
What is angina pectoris?
A sensation of pain, tightness or heaviness in the chest which may radiate to the jaw, shoulders, back or arms.
- Duration: between 2 to 10 minutes.
- Precipitating factors: symptoms usually occur during exertion, emotional stress, in the cold or after a meal.
- Relieving factors: symptoms disappear on their own with rest after 5 minutes or after taking trinitrine spray.
Other symptoms may suggest problems with the coronary arteries: shortness of breath, marked tiredness or weakness / dizziness.
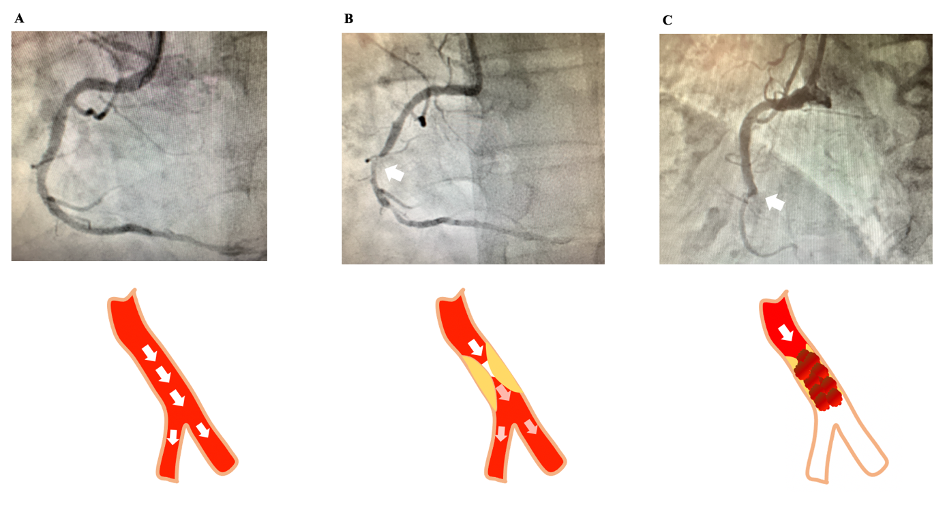
Myocardial Infarction
What happens when a coronary artery is completely blocked?
Myocardial infarction is characterized by the rupture of an atherosclerotic coronary plaque, which causes an abrupt interruption of blood flow to a specific area of the heart muscle. When a plaque rupture occurs within a coronary artery, blood components such as platelets and red blood cells will clump together to form a blood clot within the coronary artery, thus blocking normal blood circulation to the heart muscle. The lack of blood and oxygen supply to the heart generate symptoms such as angina pectoris (Figure B). Myocardial infarction or a “heart attack” occurs when the artery is occluded for a prolonged period of time (Figure C), leading to permanent damages to the heart muscle. Myocardial infarction may lead to subsequent complications, such as heart failure, ventricular arrhythmias and sudden death, a substantial burden for coronary patients. It is therefore imperative to act quickly to restore the normal blood flow in the artery in order to avoid any irreversible damage and long-term complications.